Digital tools such as telehealth, remote monitoring and mobile health apps are key to transforming health care, but trust in these new ways to provide care remains a stumbling block, University of Queensland researchers have found.
In a comprehensive review, Dr. Soraia de Camargo Catapan and Dr. Jaimon Kelly from UQ’s Center for Online Health analyzed 49 studies, published over 13 years, to identify factors influencing consumer and health care professionals’ trust in digital health care.
The research is published in npj Digital Medicine.
“If people don’t trust digital health care, they won’t use it,” Dr. Catapan said.
“Trust is inherently difficult to define and measure but it is key to making digital health tools more effective and widely used.
“Building trust can help more people use these health technologies in the long run, leading to better outcomes and making digital health care more sustainable.”
Examples of digital health care include electronic health records, wearable devices, telehealth, mobile health, and medical artificial intelligence.
The review examined studies published between 2010 and 2023, with 40% of the studies conducted in China or the United States.
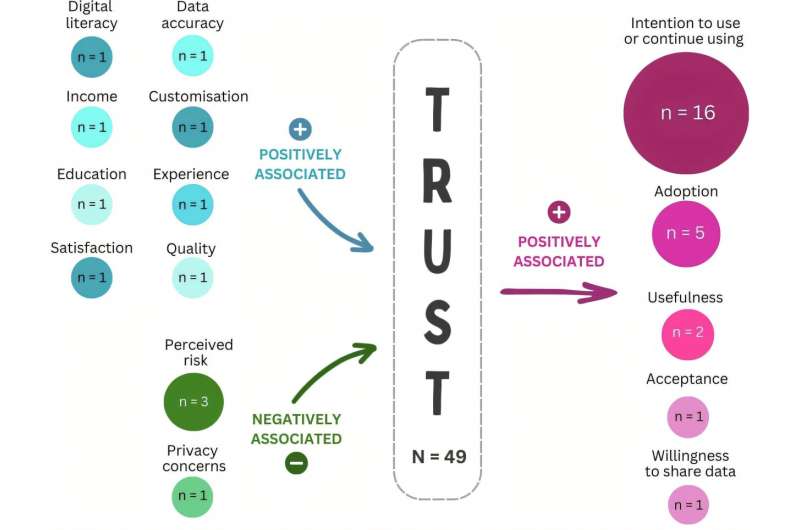
It found trust in digital health care could be influenced by a person’s digital literacy, education levels, prior experiences with digital health, income, privacy concerns and perceived risks.
The quality of digital health care, data accuracy, and the degree of human interaction in automated interventions also played a part in building trust.
Dr. Kelly said trust mattered because it directly impacted consumer behavior.
“The Australian Digital Health Blueprint and Action Plan 2023–2033 describes the role of digital health capabilities in fortifying the health care system, with one of its focal areas being the reinforcement of trust,” Dr. Kelly said.
“Our review found that trust positively correlates with consumers’ intention to use, adopt, and find digital health technologies useful.
“This research is an important step toward understanding and measuring trust in digital health care.
“Developing a comprehensive framework for trust, in turn, enhances the adoption of digital health technologies, supports better health outcomes, and strengthens the long-term sustainability of digital health care solutions.”
The review also found that cultural and geographical differences, such as in China where digital privacy is more regulated, needed to be considered because perceptions of trust could differ significantly from those in Western countries.
More information:
Soraia de Camargo Catapan et al, A systematic review of consumers’ and healthcare professionals’ trust in digital healthcare, npj Digital Medicine (2025). DOI: 10.1038/s41746-025-01510-8
Citation:
Effective digital health care depends on trust, research reveals (2025, March 18)
retrieved 18 March 2025
from https://medicalxpress.com/news/2025-03-effective-digital-health-reveals.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no
part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.


Add a Comment